4. CONTEXT OF THE ORGANIZATION
Identifying the factors affecting your company will guide you in setting up your system.
4.1 Understanding the Context of the Organization
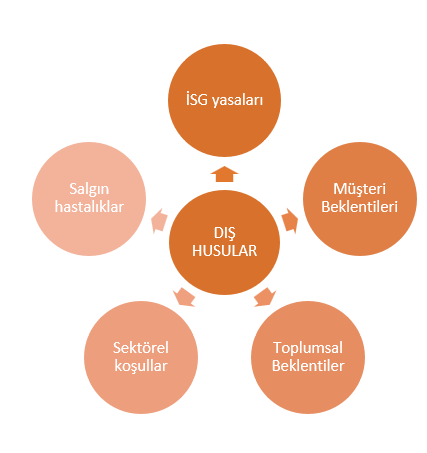
In this step, the sector in which the organization operates, the business environment, legal requirements and other external factors are examined. Factors such as the organization's founding purpose, date, size and geographical location are also taken into consideration. For this purpose, interviews can be conducted with managers, employees and external stakeholders, and industry analyzes and market research can be conducted.
For example, for a construction company, the context of the organization may include factors such as the general economic situation of the industry, competitive structure, legal regulations, occupational safety standards and project diversity.
Note: Internal and external issues are randomly sampled with a general approach, you need to customize and detail specific to the scope of your company.
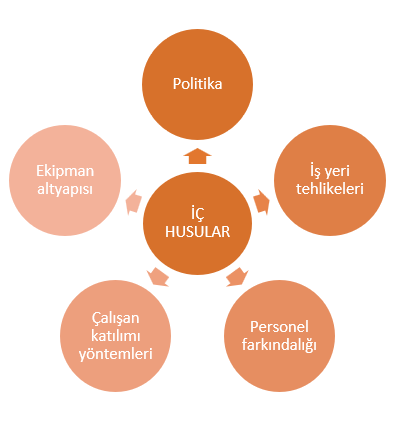
4.2 Understanding the Needs and Expectations of Employees and Other Interested Parties
4.3 Scope
The scope of the organization's Occupational Health and Safety (OHS) management system is determined. This involves defining which business units, processes or activities fall within the scope of the OH&S management system.
When determining the scope, the sector in which the organization operates, risk profile, legal regulations and stakeholder expectations should be taken into consideration.
For example, the OH&S management system scope for a factory may include specific business areas such as production line operations, warehouse activities, and office functions.
4.4 Management System and Processes
The administrative, support and operational processes necessary to improve your company's OHS performance should be determined and defined in accordance with the ISO 14001 standard . These processes may include the establishment of OSH policies, risk assessment and control, training and awareness programs, emergency planning and monitoring and measurement activities.
Processes should be constantly reviewed and updated when necessary, based on continuous improvement principles.
5. LEADERSHIP
6. PLANNING
7. SUPPORT
8. OPERATION
9. PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
10. IMPROVEMENT


Comments